Artificial Intelligence:
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to systems designed by humans that acts smartly on assigned goal. These systems act in the physical or digital world by perceiving their environment, interpreting the collected structured or unstructured data, reasoning on the knowledge derived from this data and then decides the best actions to take to achieve the given goal. In other words, AI systems can also be designed to learn to adapt their behavior by analyzing how the environment is affected by their previous actions.
Moreover, as a scientific discipline, AI includes several approaches and techniques mentioned below.
- Machine Learning – Specific examples are Deep Learning (DL), Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Machine Reasoning – Planning, Scheduling, Knowledge representation, Reasoning, Search and Optimization
- Robotics – Control, Perception, Sensors, and Actuators and Integration of all other techniques into cyber-physical systems
Artificial Intelligence Sub-fields:
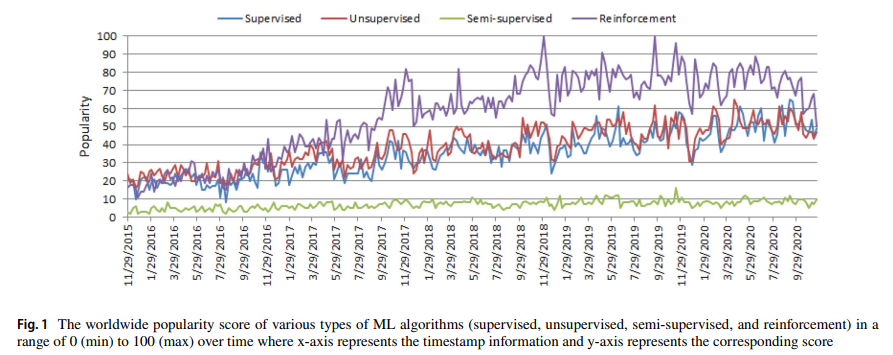
Firstly, Machine learning is the sub-field of artificial intelligence. It is a technique for making computers learn patterns and meaningful relationships through experience from observations and examples. Additionally, the algorithms of machine learning can be classified as supervised learning algorithms, unsupervised learning algorithms, semi-supervised learning algorithms, and reinforcement learning. Moreover, the following figure [4] demonstrates the worldwide popularity score of above-mentioned algorithms.
Secondly, Deep learning is a sub-field of machine learning that stores rules of learned representations of data in the form of weights and biases, and these data representations with levels of abstraction are obtained by passing data through a multi-layer neural network architecture [3]. Besides, the performance of deep learning gets better with an increased quantity of data compared to other learning algorithms in machine learning. The root of Deep Learning algorithms are Artificial Neural Networks (ANN).
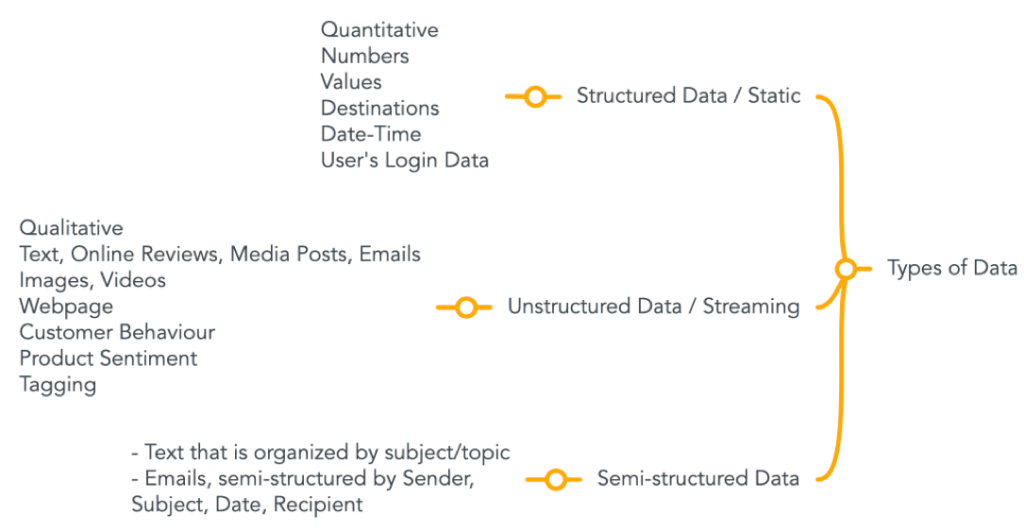
Types of Data:
What’s more? —> Data is equally important in order to get meaningful results out of machine learning algorithms. A AI solution heavily depends on the nature and characteristics of data. In 2006, Fei-Fei Li, a computer science professor at Stanford University, hypothesized that the amount of data that reflects reality is the artificial intelligence’s main limitation, and that more data will produce better models [1]. In addition to this, the outcome of different learning algorithms may differ depending on the nature and characteristics of the data. This applies to data belong to the same category.
Finally, we should talk about types of data.
Examples:
- Structured Data: Names, Dates, Stock information, Geolocation, Credit card numbers, addresses etc.
- Unstructured Data: Sensor data, PDF files, Video Files, Images, Presentations, Webpages, Tagging etc.
- Semi-structured Data: HTML, JSON documents, NoSQL databases, etc.
References:
- Delipetrev, C. Tsinaraki, and U. Kostic, “Historical evolution of artificial intelligence,” 2020.
- H. AI, “High-level expert group on artificial intelligence,” 2019.
- Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, “Deep learning,” nature, vol. 521, no. 7553, pp. 436–444, 2015.
- Sarker, Iqbal H. “Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions.” SN computer science 2.3 (2021): 160.







